Outlook for Computing Infrastructure in the AI Era NTT PR/IR DAY
NTT held its PR/IR DAY on October 6th. The main themes of the event were optical computing in the AI era, centered around IOWN, and low-power devices using photonics-electronics convergence technology.
Expanding AI usage will increase power consumption.
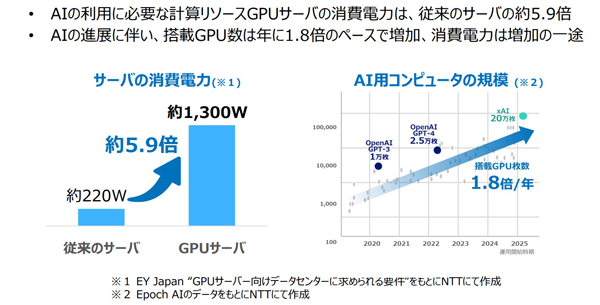
GPU servers, the computing resources required for AI, consume 5.9 times more power than conventional servers. The number of GPUs installed on servers is increasing at a rate of 1.8 times per year.
For example, it is estimated that datacenter power consumption by 2030 will exceed the current annual total power consumption of Tokyo. The rapid increase in power consumption due to the expansion of AI usage will be significant.
Given this background, efficient operation and reduced power consumption are required for computing infrastructure supporting AI utilization.
NTT Executive Vice President Sachiko Onishi stated, “IOWN will be a key component in achieving both efficient AI operation and reduced power consumption.”
The computing infrastructure that will support the AI era will be realized by connecting massive amounts of distributed GPU resources at high speed using the IOWN APN to create a single, virtually gigantic computing platform.
Stable operation will be possible by flexibly allocating distributed computing resources, such as GPUs, to locations that can provide the necessary power supply based on computing resource optimization, GPU load, and power consumption.
Furthermore, it is essential to reduce the power consumption of the equipment that makes up the infrastructure.
As AI processing volume increases, more GPUs are required, and so will intra-computer communications. Electrical communications have their limits, so this portion must be converted to optical communications.
This is made possible by IOWN2.0, or photonics-electronic convergence devices.
Electricity’s frequency increases with communication speed, and so does power consumption. As the number of GPU servers increases and the amount of communication between them increases, electricity consumption also increases dramatically.
On the other hand, with optical communications, power consumption remains constant even as communication speeds increase. Utilizing optical communications is the only way to achieve both increased communication capacity and reduced power consumption.
NTT will begin commercially deploying photonic-electronic converged switches from 2026. The company says it will work in collaboration with overseas companies such as Broadcom and Acton. NTT plans to coordinate the entire project and build a supply chain.
NTT President Akira Shimada said, “The most important point of IOWN is reducing power consumption. Photonic-electronic converged devices are at the heart of this effort. Through this NTT PR/IR DAY, we were able to demonstrate that NTT is not promoting IOWN alone, but is moving forward together with partners around the world.”
※Translating Japanese articles into English with AI