APN reduces data center load NTT, NTT West, and QTnet
NTT, NTT West, and QTnet have jointly demonstrated that it is possible to utilize the large capacity and low latency features of the IOWN APN to optimize processing placement (dynamically optimize processing placement according to calculation load and power consumption) even in a computing environment distributed across geographically distant data centers.
As is well known, AI is currently in the spotlight, and demand for data centers is expanding. As a result, power consumption has become an issue, and expectations are high for carbon neutrality and reduced environmental impact through renewable energy. On the other hand, renewable energy is said to be difficult to control, and output control is actually occurring. Output control is the temporary suppression or halt of power generation in order to maintain a balance between power demand and supply. In fiscal 2023, output control was carried out nationwide on approximately 1.9 billion kilowatts per year. In particular, Kyushu has been actively introducing renewable energy, and output control has occurred frequently.
This demonstration was conducted with the aim of solving these issues by combining APN and other technologies.
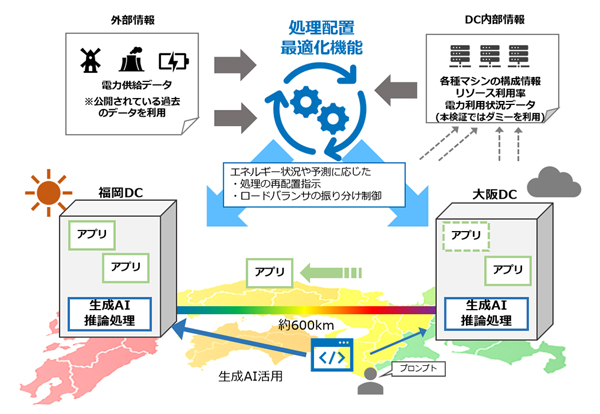
First, to verify the execution of processing placement optimization, the data centers in Fukuoka and Osaka (600 km) were connected by APN, and a distributed data center environment consisting of a virtualization platform and a generation AI platform on which applications were placed was constructed. Previously, downtime that affected applications was an issue when changing placement without stopping the application.
Yoshida Koyo of the IOWN Promotion Office, Technology Innovation Department, Digital Innovation Headquarters, NTT West Japan explains, “This type of configuration is not possible with ordinary lines, but a large-capacity, low-latency APN makes it possible to create a distributed data center environment with reduced downtime. This has created a foundation for integrated operation, such as moving applications.”
The processing placement optimization function developed by NTT Laboratories was operated on this foundation. The processing placement optimization function calculates the optimal control, such as running this process here and this process there, according to external information.
As a result, they were able to create a schedule in which, since Fukuoka’s renewable energy output is large, it is operated in Fukuoka during the day, and then switched between Osaka and Fukuoka after dark to distribute the load. They also confirmed that processing was being moved appropriately.
“In this demonstration, the utilization rate of renewable energy increased by 31%. The figures will vary depending on the number of data centers and the energy output situation, but we were able to confirm that processing is feasible. We believe that this will promote the use of renewable energy in data centers and reduce the environmental burden,” says Yoshida.
This demonstration also confirmed that new value can be created by combining APN with other technologies.
Yoshida says, “We would like to continue combining APN with other technologies to work on use cases that add value.”