7th draft “EE function-construction theory” Hideya Inoue (business structure analysis consultant)
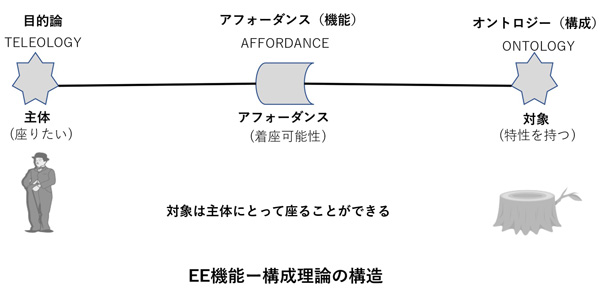

EE function-construction theory is a theory about how subjects (people) perceive things around them.
It is based on Gibson’s affordance theory. It explains the division between function and construction, the meaning of artifacts, experience and value, and white/black boxes.
Affordance is defined as the possibility of action in the natural world. For example, the affordance of a stump can be said to be that a human can “sit” on it. In this case, if the subject does not want to sit, he or she may not recognize the affordance that the stump provides. Affordance occurs when the needs of a subject with a purpose match the properties of the object. In this case, the structure of the thing, the stump (ontology), provides the affordance of being able to sit on it, satisfying the subject’s needs, which are subjective (teleology). This relationship is shown in the diagram on the upper left.
This theory also relates to creating artifacts. The affordances that an artifact provides are called functions. An artifact has not only intended functions, but also unintended functions, because function is the relationship between the subject and the object. The concept of affordance is important as it also influences discussions on how to handle artificial intelligence, which is an artifact.
Furthermore, this theory prescribes the concepts of experience and value. Experience means the subjective sensation evoked in the mind of the subject when perceiving an affordance. Value is the strength of the experience evoked in the mind of the subject by recognizing an affordance. On the other hand, price is the nature of an object.
When function and configuration are contrasted in terms of the relationship between parts, another classification method for models emerges. A system is made up of an assembly of components, and conversely, it can be decomposed into parts, and this relationship creates a type of constructive tree. When this concept is applied to functions, a functional tree is obtained, but since functions are subjective, there are types of this tree proportional to the number of subjective perceptions. A constructive tree is called a white box model, and a functional tree is called a black box model. Furthermore, white-box models with internal functions are called gray-box models. These models can be defined in mathematical logic.
The human brain has an amazing ability to generate various concepts by perceiving things.
※Translating Japanese articles into English with AI