Estimating future changes in electricity consumption National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) is collaborating with Meisei University and Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings to clarify the actual state of electricity consumption in the Tokyo metropolitan area as part of an assessment of the impact on energy consumption during extremely high temperatures. They estimated future changes in electricity consumption due to climate change.
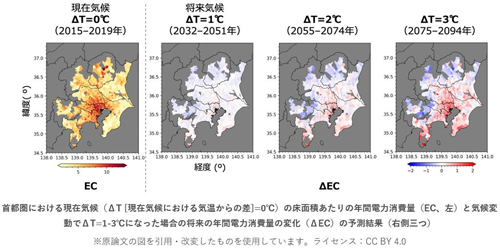
The results showed that future global warming could significantly increase electricity consumption, especially in office blocks in urban areas.
The amount of change in electricity consumption was estimated based on detailed electricity consumption big data in the Tokyo metropolitan area and global warming prediction technology. By combining this estimation method with an urban climate model developed independently by AIST, it has become possible to estimate how future electricity consumption may change as decarbonization technologies become more widespread.
Assuming that decarbonization technology becomes widespread in the future, it is possible that the increase in electricity demand due to the use of air conditioners in buildings in urban areas could be cut in half. It was shown that if the power source mix remains unchanged in the future, the increase in CO2 emissions from electricity can be reduced to about half.