Hitachi proposes “shutling qubit method” aiming at commercialization of silicon quantum computer
Aiming for the practical use of silicon quantum computers, Hitachi has proposed a “shutling qubit method” that can efficiently control qubits, and has confirmed its effectiveness.
The keys to the practical use of quantum computers are the large-scale integration of one million quantum bits or more and the realization of error correction on that basis.
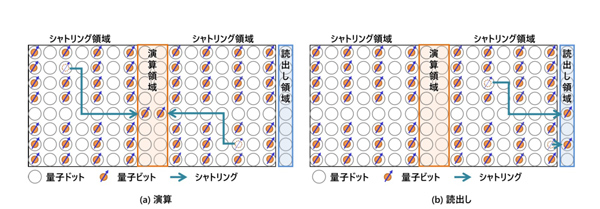
Silicon quantum computers, which Hitachi is researching and developing, are said to be more advantageous in terms of scale-up than superconducting computers, which are currently being developed. However, since qubits are generally installed in fixed locations, it is necessary to connect operation and readout circuits to all qubits, and errors can occur between adjacent qubits. This was a factor that hindered scale integration.
In the shuttling qubit method, it is possible to set a region in which control such as calculation and reading is performed in advance, and to freely move the qubit between them. This eliminates the need to connect operation and readout circuits to all qubits, simplifies the wiring structure of silicon devices, and suppresses the effects of errors by evacuating adjacent qubits for operations.