Build MHI to support safe driving based on brain research Honda R&D and Araya
Honda R&D and Araya announced at the 27th ESV International Conference the results of a demonstration experiment of a system that identifies parts related to safe driving from brain activity while driving and uses AI to inform drivers of risk factors. bottom.
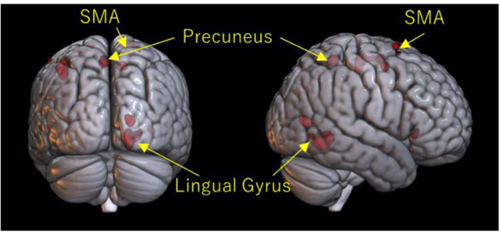
When extracting the difference in brain activity when encountering risk between risk minimum drivers and general drivers, it was confirmed that there was a significant difference in activity in the part called the precuneus.
As a result, it was suggested that drivers who are at high risk for safe driving have low spatial awareness and cannot predict danger because they cannot see it, which is a risk factor. It was also suggested that they judge risks based on the memories and knowledge they have experienced.
Based on this research, Honda R&D has constructed a human machine interface (MHI) that complements the cognitive processing necessary for safe driving and assists drivers. To verify the effectiveness of the HMI, experiments were conducted using a driving simulator consisting of the front of the vehicle and five displays. As a result, it was found that HMI has the effect of recognizing and avoiding high-risk objects at an early stage, and it was demonstrated that HMI can supplement and support cognitive processing necessary for safe driving.